Restore Your Energy in Minutes with Yoga Nidra

Feeling overwhelmed by the constant demands of modern life? The pressure to always be available, connected, and exuding positive energy can take a serious toll on our health. Brain fog, stress, fatigue, anxiety, and sleep problems have become more common than ever before. While the complexity of these issues might seem daunting, there’s a simple yet highly effective practice that can help alleviate these symptoms: Yoga Nidra. This ancient technique offers profound relaxation and restoration, allowing you to reclaim your well-being and inner peace.
What is Yoga Nidra?
Yoga Nidra, often referred to as “yogic sleep,” is a guided meditation practice that induces deep relaxation while maintaining a state of consciousness. Despite its name, Yoga Nidra is not about falling asleep but rather about reaching a state of consciousness that is between wakefulness and sleep. In this state, deep healing can occur.
Yoga Nidra was introduced by Swami Satyananda Saraswati, the visionary founder of the Bihar School of Yoga, in the early 1960s. Drawing from ancient practices within the yoga tradition, Satyananda adapted and refined these techniques, making them accessible to the general public.
Yoga Nidra Structure
There are numerous ways of practicing Yoga Nidra. However, nearly all sessions more or less follow a structured format designed to lead practitioners into a state of profound rest and rejuvenation. A typical Yoga Nidra practice follows a general path consisting of 8 Stages (Steps):
- Preparation and Initial Relaxation
- Sankalpa
- Body Awareness
- Breath Awareness
- Experience Of Opposite Sensations
- Visualization
- Revisiting Sankalpa
- Returning In The Body
Let’s unpack each of these stages.
Preparation and Initial Relaxation
The practice begins with a few moments of relaxation, focusing on releasing tension from the body and calming the mind. You are invited to lie down in a comfortable position, usually savasana (corpse pose), with your eyes closed. Make any adjustments necessary to ensure you are completely comfortable and supported.
Sankalpa
Identify an intention that resonates with your deepest desires and aspirations. Such an intention is known as Sankalpa. There are several principles for formulating a sankalpa:
- It consists of a short, concise positive sentence
- It is aimed at being instead of having or possessing
- It is formulated in the present and not in the future tense.
Some examples of a sankalpa could be: “I am lovable and kind to the people surrounding me”, or : “I’m truthful to myself at every moment”. Establishing a sankalpa aids in training your mind to maintain focus, infusing the practice with greater purpose and direction.
Body Awareness (Rotation of Consciousness)
The heart of the Yoga Nidra practice is the body scan, also known as the rotation of consciousness. In this stage you will be guided through a systematic journey of body awareness, directing attention to different parts of the body one by one. This process promotes deep relaxation and allows you to release physical tension.
Breath Awareness
Following body awareness you’ll be encouraged to establish awareness of your breath. You may be guided to observe the natural rhythm of your breath. Or you may be encouraged to notice the inhalations and exhalations as they flow effortlessly in and out of the body. One of the breath awareness techniques in Yoga Nidra is counting each breath in reverse order. With each inhalation and exhalation, you count backward, guiding yourself toward a state of calm.
Breath awareness helps to anchor the mind in the present moment and deepen the state of relaxation.
Experience Of Opposite Sensations
In this phase, you encounter contrasting sensations within your body, such as hot / cold or heavy/light, love / hate, etc. By intently reviving certain body sensations and emotions you can become more aware of them and learn to better control them. Through regular practice, you can identify and release thought patterns that don’t serve us anymore.
Visualization
Yoga Nidra often incorporates visualizations to stimulate the subconscious mind. You may be guided to envision an image representing some personal or universal archetypes , e.g. a cross, a half moon, a mountain, a desert, sunset, a grave, the sun, etc.. You can also be guided to imagine yourself in a peaceful natural setting, such as a serene beach or lush forest, or to visualize sensations of warmth and light spreading throughout your body. These visualizations can help uncover and release suppressed feelings and emotions.
Revisiting Sankalpa
Towards the end of the practice, you are invited to revisit your sankalpa, repeating it silently to yourself with deep conviction and sincerity. By reaffirming your intention in this deeply relaxed state, you plant the seeds of positive change in their subconscious mind, aligning yourself with your highest aspirations and goals.
Returning In The Body
As the Yoga Nidra practice comes to a close, you will be gently guided back to a state of wakefulness. This includes returning to your body, your breath, your feelings, your thoughts, and to the external environment.
Yoga Nidra and Brain
As the Yoga Nidra practice comes to a close, you will be gently guided back to a state of wakefulness. This includes returning to your body, your breath, your feelings, your thoughts, and to the external environment.
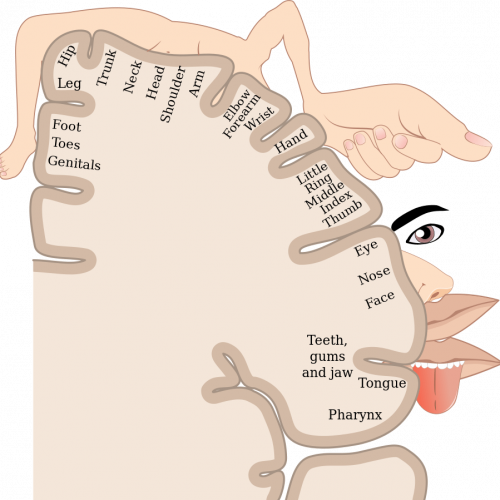
The Sensory Homunculus
During the third stage of Yoga Nidra (Body Awareness), we engage in a process called rotation of consciousness. This is a kind of body scanning, during which practitioners systematically move their awareness through different parts of the body in a specific order. This technique is deeply connected to the concept of the sensory homunculus. The sensory homunculus illustrates how much cortical space is dedicated to processing sensory input from different parts of the body. It’s like a map of the body within the brain, with larger areas devoted to body parts that have more sensory receptors and finer discrimination abilities. For example, the hands, lips, and face have larger representations in the sensory cortex compared to areas like the back or legs.
By directing attention to each part of the body and moving from one area to another during the rotation of consciousness we stimulate the corresponding regions of the sensory cortex, activating neural pathways associated with sensory perception and awareness.
As we focus our attention on each body part, we may notice sensations such as warmth, tingling, or relaxation in that area. This heightened sensory awareness helps to deepen the relaxation response to feel more connected to our own body.
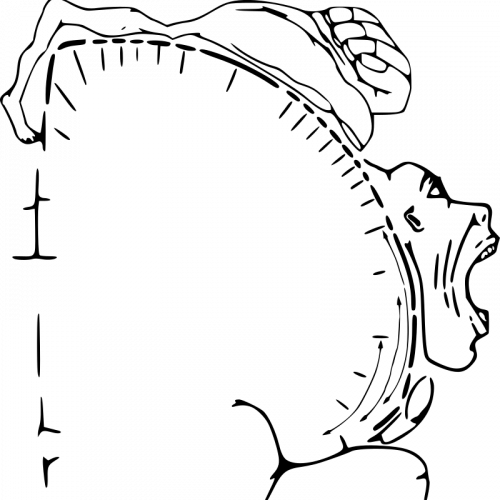
The Motor Homunculus
The rotation of consciousness can also be connected to the concept of the motor homunculus, which represents the relative amount of cortical space devoted to controlling movements of different body parts. While the primary focus of Yoga Nidra is on sensory awareness and relaxation, the intentional movement of attention through different body regions can also influence motor control and proprioception.
By systematically directing attention to each body part, we may enhance our awareness of subtle movements and sensations, leading to improvements in motor coordination and body awareness over time.
This integration of sensory and motor processes contributes to the overall effectiveness of Yoga Nidra as a practice for promoting relaxation and mind-body connection.
Benefits of Yoga Nidra
The benefits of Yoga Nidra are immense. Here are some of them:
- Energy Restoration: Even a short session of Yoga Nidra can leave you feeling refreshed and energized, making it the perfect remedy when you’re running on empty.
- Stress Reduction: Life often brings its share of stress and worry. Yoga Nidra helps calm the nervous system, promoting inner peace and relaxation.
- Improvement of Sleep Quality: By inducing deep relaxation, Yoga Nidra can help you fall asleep more easily and enjoy a more restful night’s sleep. Unless, of course, you have a baby or a naughty toddler who keeps you awake and occupied
- Greater Mental Clarity: Restless sleep can leave you feeling foggy-headed and forgetful. Yoga Nidra clears the mind, improves focus, enhances mental clarity, and helps you tackle daily tasks with greater efficiency.
- Better Emotional Well-Being: Adult life can be emotionally demanding, so caring for your mental and emotional well-being is essential. Yoga Nidra fosters inner balance and emotional resilience, helping you navigate life’s ups and downs with greater ease.
Conclusion
Yoga Nidra is a powerful tool for restoring energy and finding moments of peace amidst daily stress. By practicing Yoga Nidra regularly, we can tap into a well of relaxation and show up as the best version of ourselves. So, the next time you find yourself feeling exhausted and overwhelmed, carve out a few minutes for Yoga Nidra and experience the restorative power of yogic sleep.

Are you interested in yoga, fitness, and personal development? So am I! Are you trying to juggle parenthood and work? Me too! In my blog, I write about all these topics (and more!) as I want to help working parents find energy, strength, and balance in life.

